Biotechnology and AI: Technological Convergence and Information Hazards (Part 2)
Part 2 summarizing chapters from "Biotechnology and AI: Technological Convergence and Information Hazards" from the NATO Advanced Research Workshop on AI and biotechnology convergence
Last week I posted part 1 summarizing the first few chapters of Biotechnology and AI: Technological Convergence and Information Hazards, which came out of an Advanced Research Workshop as part of the NATO Science for Peace and Security (SPS) series, where international experts gathered to address the dual-use nature of these emerging technologies.
Here’s a quick look at the remaining chapters I didn’t get a chance to summarize last week.
Governance Frameworks and Scenario Evaluation Exercises on AI and SB Ethical Dilemmas
Cruz, J. C., Mampuys, R., Reyes, G., & Dryhurst, S. (2026). Governance Frameworks and Scenario Evaluation Exercises on AI and SB Ethical Dilemmas. In C. L. Cummings, B. D. Trump, V. Prado, B. Ellinport, & I. Linkov (Eds.), Biotechnology and AI: Technological Convergence and Information Hazards (pp. 109–167). Springer Nature Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-032-05246-9_6
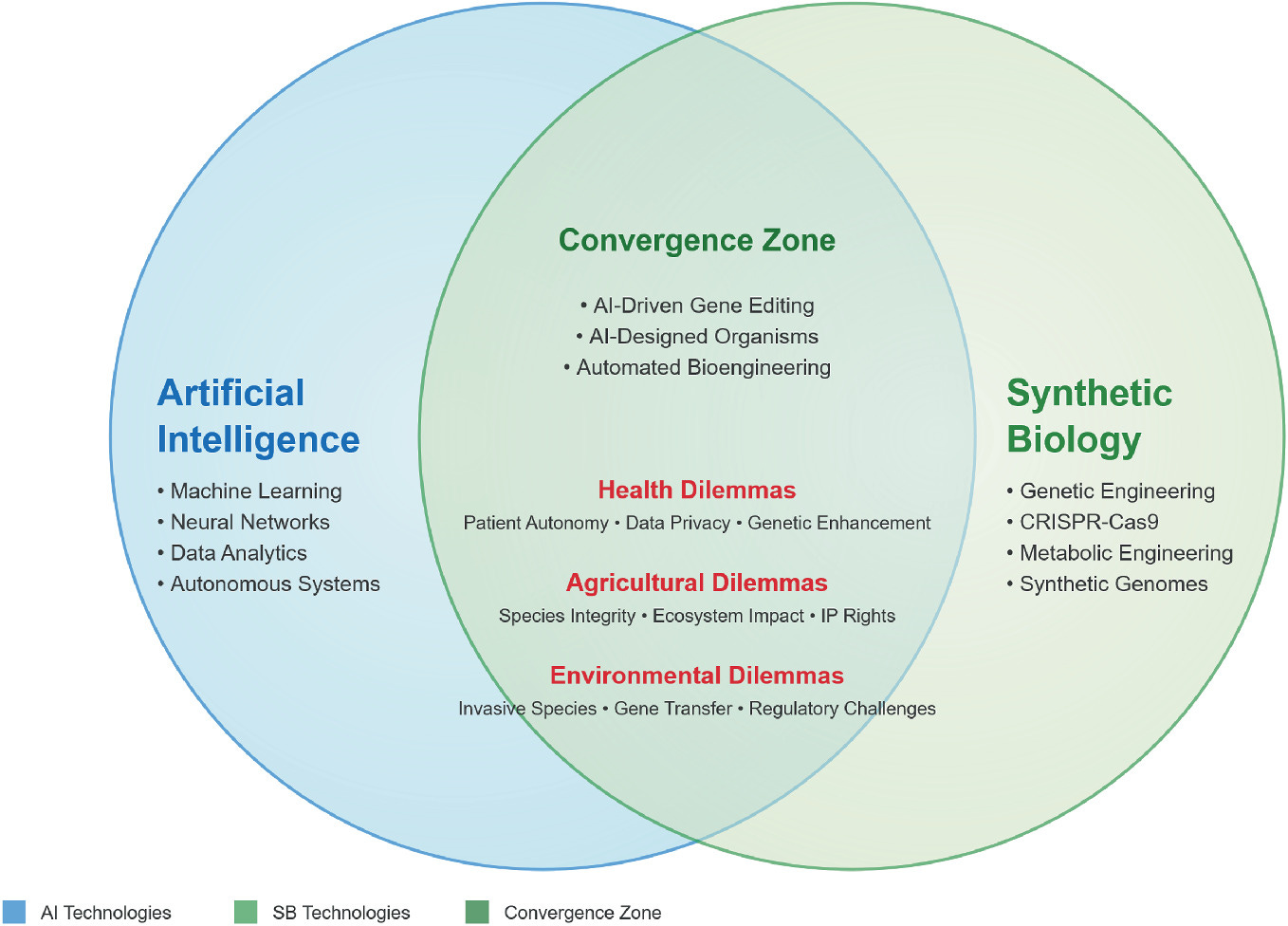
The chapter utilizes scenario-based exercises to help stakeholders navigate the complex ethical dilemmas presented by the convergence of artificial intelligence and synthetic biology. It advocates for inclusive governance that incorporates diverse perspectives from scientists, ethicists, and affected communities to guide the responsible deployment of synthetic organisms.
Ethical Implications and Governance Solutions for the Convergence of AI and Synthetic Biology in Healthcare and Agriculture.
Cruz, J. C., Mampuys, R., Reyes, G., & Dryhurst, S. (2026). Ethical Implications and Governance Solutions for the Convergence of AI and Synthetic Biology in Healthcare and Agriculture. In C. L. Cummings, B. D. Trump, V. Prado, B. Ellinport, & I. Linkov (Eds.), Biotechnology and AI: Technological Convergence and Information Hazards (pp. 169–215). Springer Nature Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-032-05246-9_7
This chapter explores the ethical challenges specific to precision medicine and agricultural bioengineering, such as data privacy and child autonomy in genetic interventions. It offers practical governance solutions to ensure these technologies advance human health and food security without compromising human rights or essential ethical standards.
Assessing Governance and Regulatory Frameworks for Converging Technologies: The Case of Artificial Intelligence in Biological Engineering and Design Technologies
Nichols, G. P. (2026). Assessing Governance and Regulatory Frameworks for Converging Technologies: The Case of Artificial Intelligence in Biological Engineering and Design Technologies. In C. L. Cummings, B. D. Trump, V. Prado, B. Ellinport, & I. Linkov (Eds.), Biotechnology and AI: Technological Convergence and Information Hazards (pp. 217–236). Springer Nature Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-032-05246-9_8
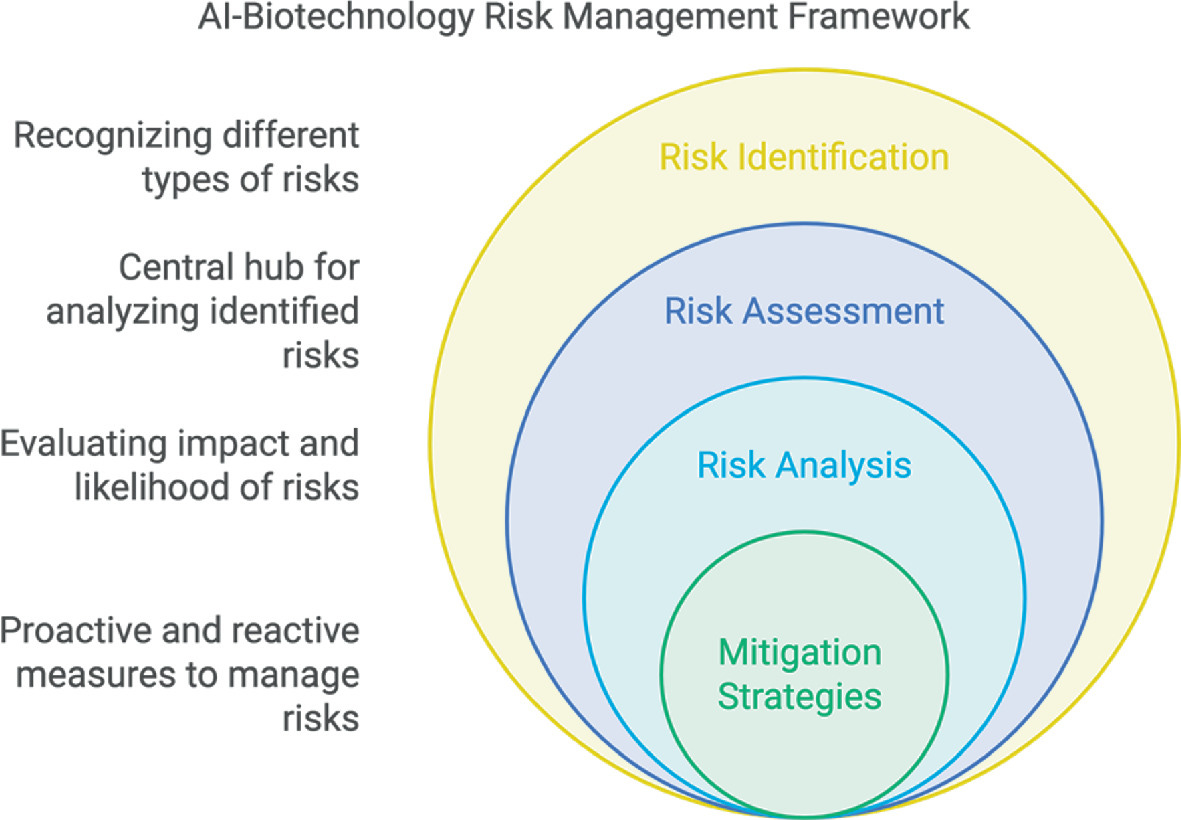
The author analyzes existing regulatory frameworks and highlights significant gaps in addressing the unique challenges posed by hybrid technologies. It argues for clearer definitions and stronger authority in governing the intersection of artificial intelligence and biological design to mitigate potential environmental or societal harm.
Non-genetic Optoelectronic Biointerfaces
Li, P., & Tian, B. (2026). Non-genetic Optoelectronic Biointerfaces. In C. L. Cummings, B. D. Trump, V. Prado, B. Ellinport, & I. Linkov (Eds.), Biotechnology and AI: Technological Convergence and Information Hazards (pp. 237–257). Springer Nature Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-032-05246-9_9
This chapter discusses the technical development of biointerfaces that use light and electronics to interact with biological systems without requiring genetic modifications. It examines the potential for these tools to provide innovative medical treatments while sidestepping some of the ethical and regulatory hurdles associated with gene editing.
Synergizing Minds and Machines: Harnessing Generative AI for Transformative Biotechnology Education
Cruz, J. C., & Reyes, L. H. (2026). Synergizing Minds and Machines: Harnessing Generative AI for Transformative Biotechnology Education. In C. L. Cummings, B. D. Trump, V. Prado, B. Ellinport, & I. Linkov (Eds.), Biotechnology and AI: Technological Convergence and Information Hazards (pp. 297–327). Springer Nature Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-032-05246-9_12
Harnessing Generative AI for Transformative Biotechnology Education This chapter introduces the Cognitive-AI Synergy Framework as a roadmap for responsibly integrating generative artificial intelligence into biotechnology teaching. It provides practical strategies for using AI to enhance student learning outcomes while maintaining critical human oversight and ensuring ethical standards are upheld in the classroom.
AlphaFold and the Protein-Folding Problem
Stevens, H. (2026). AlphaFold and the Protein-Folding Problem. In C. L. Cummings, B. D. Trump, V. Prado, B. Ellinport, & I. Linkov (Eds.), Biotechnology and AI: Technological Convergence and Information Hazards (pp. 259–273). Springer Nature Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-032-05246-9_10
The chapter details how DeepMind’s AlphaFold used artificial intelligence to solve the long-standing protein-folding problem, marking a major breakthrough in structural biology. It discusses how this achievement is shifting the field toward data-driven engineering and raising questions about the role of commercial labs versus academic institutions in fundamental science.
Bridging the Biotechnology Valley of Death: Modernizing the TRL-MRL-IRL Acquisitions Process for Accelerated Technology Modernization
Trump, B. D., & Horgan, M. D. (2026). Bridging the Biotechnology Valley of Death: Modernizing the TRL-MRL-IRL Acquisitions Process for Accelerated Technology Modernization. In C. L. Cummings, B. D. Trump, V. Prado, B. Ellinport, & I. Linkov (Eds.), Biotechnology and AI: Technological Convergence and Information Hazards (pp. 275–295). Springer Nature Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-032-05246-9_11
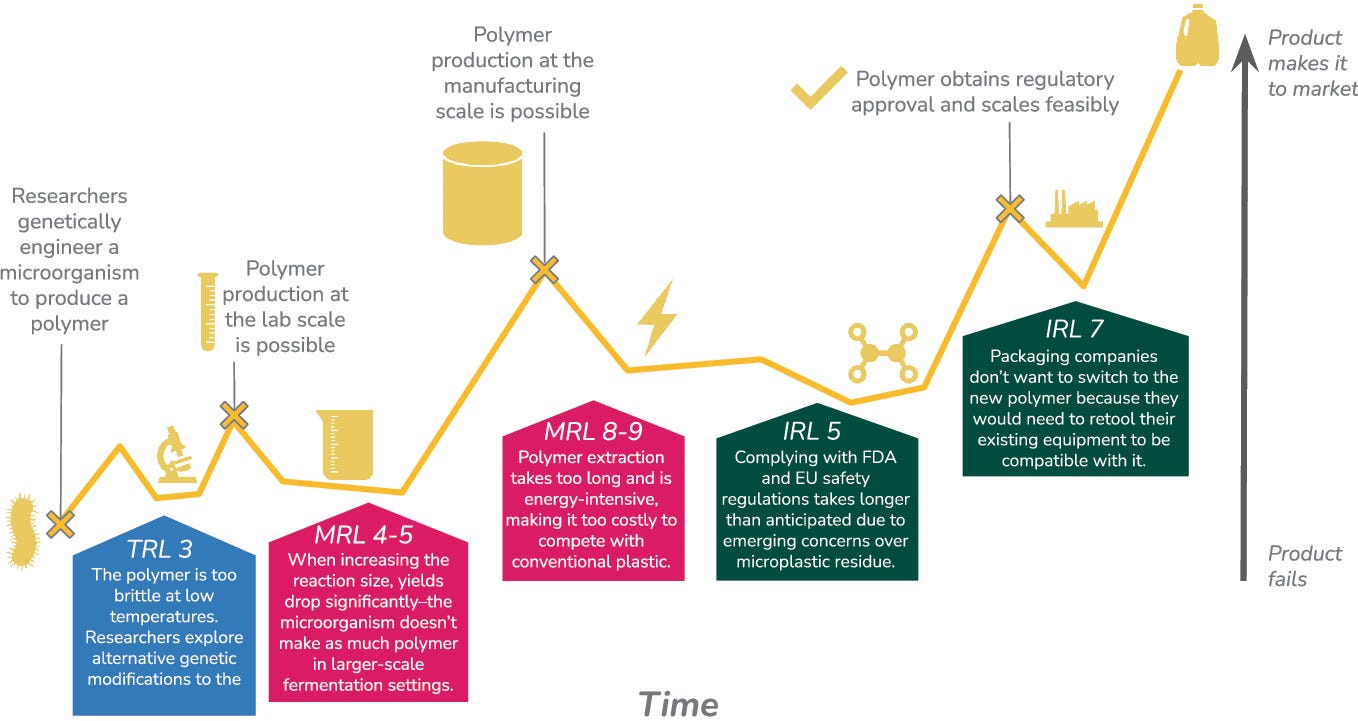
The authors propose modernizing technology and manufacturing readiness levels to help biotechnological innovations transition from laboratory research to practical application. This chapter focuses on accelerating the deployment of advanced biological tools within defense and industry acquisition systems to overcome the transition gap known as the valley of death.
Data Diversity and Sequence Length: Key Levers for Powerful Biological AI
Kozma, L., & Hoarfrost, A. (2026). Data Diversity and Sequence Length: Key Levers for Powerful Biological AI. In C. L. Cummings, B. D. Trump, V. Prado, B. Ellinport, & I. Linkov (Eds.), Biotechnology and AI: Technological Convergence and Information Hazards (pp. 329–344). Springer Nature Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-032-05246-9_13
The chapter identifies dataset diversity and the capacity for long-context sequence modeling as the primary technical drivers for building effective biological foundation models. It concludes that mastering these technical levers is essential for strategic security, pandemic preparedness, and maintaining a technological edge within international alliances.