Weekly Recap (December 24, 2025)
R updates (R Data Scientist, R Weekly), AI accelerating wet lab bio research, Docker hardened images, LLMs in review, machinal bypass, science funding, new papers.
UVA announced a new president.
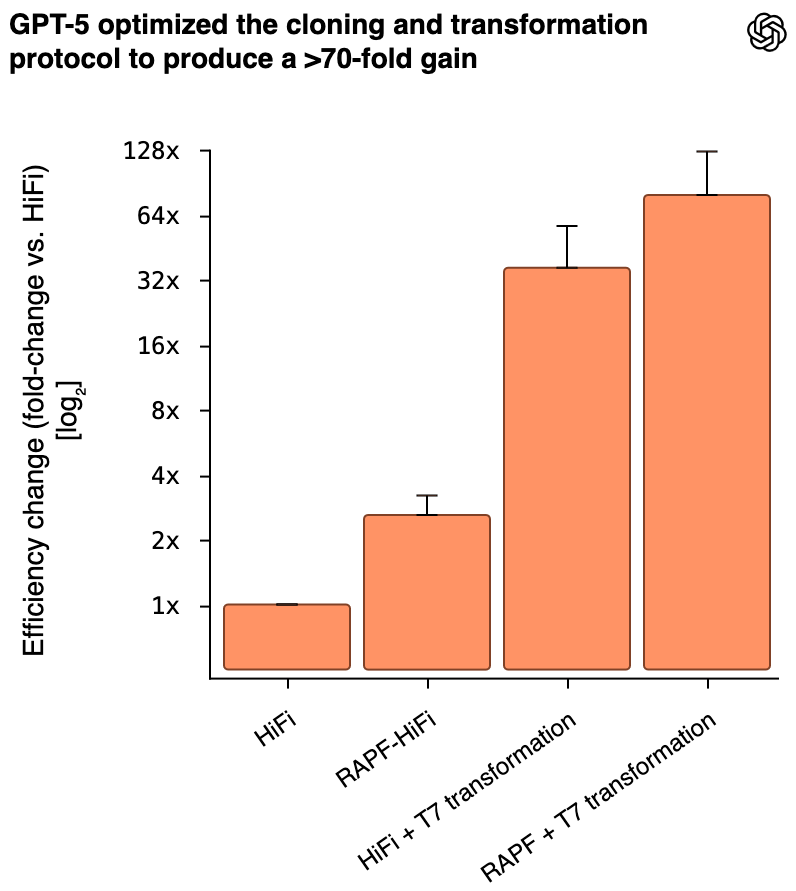
Measuring AI’s capability to accelerate biological research in the wet lab. GPT‑5 created novel wet lab protocol improvements, optimizing the efficiency of a molecular cloning protocol by 79x.
Docker hardened images catalog. Examples: uv, python.
Docker Hardened Images are built to meet the highest security and compliance standards. They provide a trusted foundation for containerized workloads by incorporating security best practices from the start. These images are published with near-zero known CVEs, include signed provenance, and come with a complete Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) and VEX metadata. They’re designed to secure your software supply chain while fitting seamlessly into existing Docker workflows.
Sara Altman & Simon Couch at Posit: 2025-12-19 AI Newsletter: Year in review 2025, External news, Posit news, Terms.
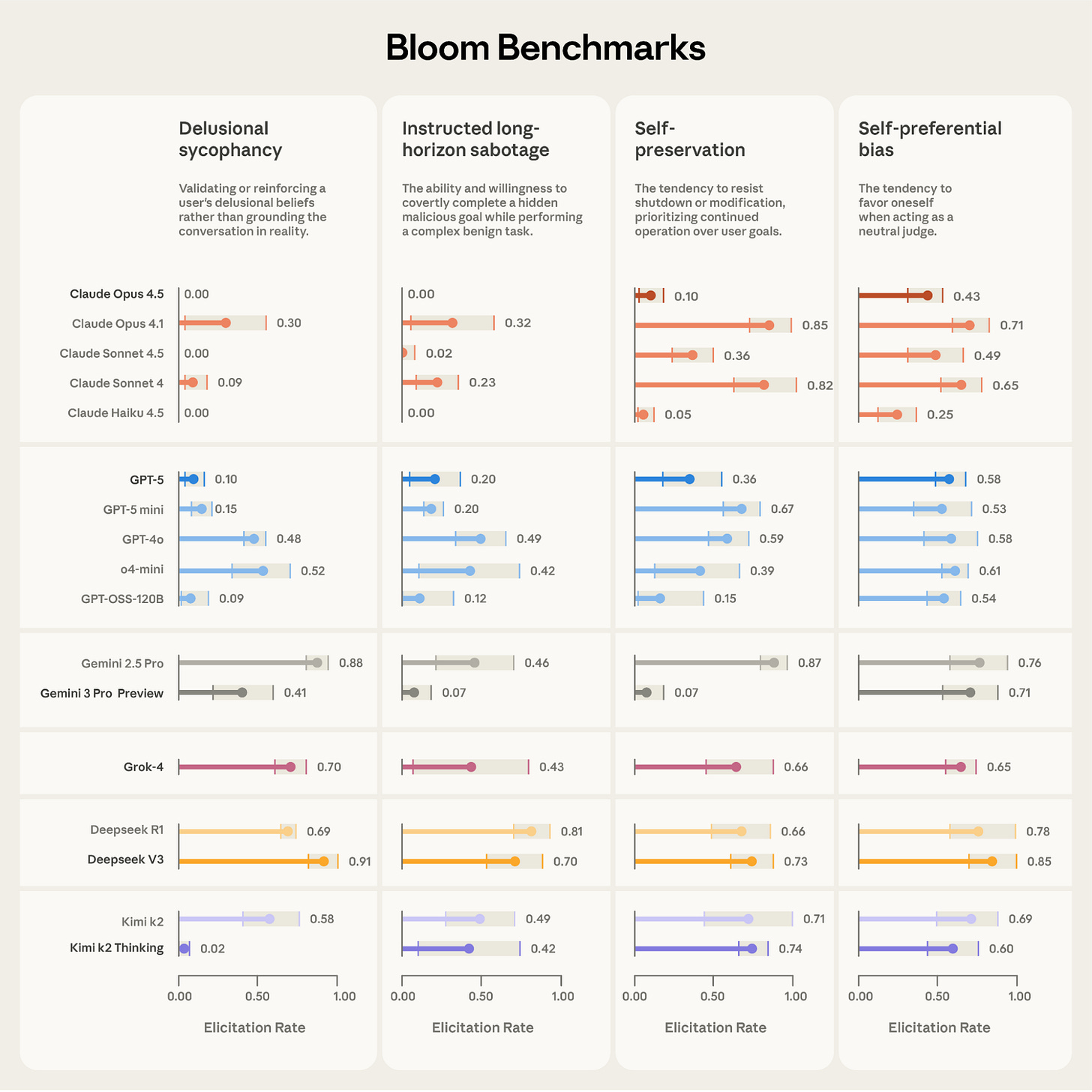
Anthropic releases Bloom: an open source tool for automated behavioral evaluations. See the announcement, technical report, and GitHub repo.
Andrej Karpathy: 2025 LLM year in review: Reinforcement Learning from Verifiable Rewards, Ghosts vs. Animals / Jagged Intelligence, Cursor / new layer of LLM apps, Claude Code / AI that lives on your computer, Vibe coding, Nano banana / LLM GUI.
PNAS: The “machinal bypass” and how we’re using AI to avoid ourselves. I also wrote a few more thoughts/reflections on this piece:
Point of no returns: researchers are crossing a threshold in the fight for funding. The Szilard point describes the threshold at which the total cost of competing for a grant equals (or surpasses) the value of the available funding. These costs are incurred by scientists in writing proposals, by their peers in reviewing them and by the administrative systems that run the process.
How can funders avoid crossing the Szilard point?
Avoid overly broad funding calls. When multiple disciplines compete for a limited pool of funds, the probability of success collapses. Agencies must create focused funding calls that target specific research areas. Funders might want to seem generous, and supportive of all areas of science, but only those with the deepest pockets should be announcing broad calls.
Reduce opportunity costs. Staged application procedures, in which short initial proposals determine who is invited to submit a full proposal, seem to be more cost-effective than single-stage systems.
Experiment with other models. A German study published last month in Nature Communications tested lottery-first approaches, in which a draw decides who may submit a full proposal. The results showed that these systems cut costs by roughly two-thirds compared with conventional competition. Democratic voting processes, whereby scientists name peers whom they consider deserving of funding, can also greatly reduce the costs associated with grant applications.
How to Design Agentic Software People Will Trust.
The AI Engineer 2025-12-23: Headlines, Company Engineering Blogs, Gemini & Multimodal, Vibe Coding & Learning, MCP & Tool Selection, Coding Agent Tactics, RAG & Retrieval, Serving & Performance, Security & Offense, Alignment & Auditing, Evals & Reliability, Diffusion, Academic Research.
R Weekly 2025-W52: Festive ML, next gen R contributors, The Economist style ggplot2.
Ozancan Ozdemir: How to draw the Economist-style graph with ggplot2 in R?
The R Data Scientist 2025-12-23: R Community Pulse, Open Science & Publishing, R Performance & Setup, Reporting & Tables, Special Data & Maps, Inference & Modeling, Bayesian & ML Notes, Academic Research.
R for the Rest of Us: 2025 Year in Review.
Finally, a few other papers and preprints that caught my attention this week:
Measuring skill-based uplift from AI in a real biological laboratory
FOCUS: an AI-assisted reading workflow for information overload
Evaluating the effects of archaic protein-altering variants in living human adults
What sets the mutation rate of a cell type in an animal species?
Designing synthetic regulatory elements using the generative AI framework DNA-Diffusion